Spring cloud data flow server is used to execute any batch job, command line task or streams as a microservice. Here we will learn how to register and execute a batch job with spring cloud data flow server. These jobs will be executed in separate JVM which gets created and destroyed on demand by spring cloud data flow server.
https://www.thetechnojournals.com/2019/12/setting-up-spring-cloud-data-flow-server.html
Put below annotation on your Spring boot main class.
Batch data source configuration
As both Spring batch job and Spring cloud data flow server uses some database to keep the data pertaining to the batch job or cloud tasks along with their execution state and context data. You will see the below error while executing the tasks if both of them not pointing to same database.
Once task is launched, we can check them at Tasks>Executions on data flow UI dashboard. Click on the ID link to check the status of your task execution.
Then, you will see below screen where you can check the status of your job. Scroll this screen to reach the bottom and there you will see the application execution log of your batch job as given here. In my case I have registered an application with two jobs which you can see in application logs screenshot executed successfully. In ideal scenario we have only one job to execute per application.
Other posts you may like to explore:
Configure multiple datasource with Spring boot, batch and cloud task
How to setup spring cloud data flow server
Please refer below post on how to setup cloud data flow server.https://www.thetechnojournals.com/2019/12/setting-up-spring-cloud-data-flow-server.html
Spring batch job
Spring batch job is used for the batch processing or background job execution where we want to process the limited set of data. I will not show how to create batch jobs in this tutorial but we will learn what is required to register your batch job with spring cloud data flow server and how to execute it then.Spring batch job registration with cloud data flow server
To register a spring batch job we need to enable the task. Below are the steps required.Enable task in your batch application
- Add below maven dependency for the task.
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-task</artifactId>
</dependency>
@EnableTask
Error starting ApplicationContext. To display the conditions report re-run your application with 'debug' enabled. 2019-12-08 15:13:57.058 ERROR 12396 --- [ main] o.s.boot.SpringApplication : Application run failed org.springframework.context.ApplicationContextException: Failed to start bean 'taskLifecycleListener'; nested exception is java.lang.IllegalArgumentException: Invalid TaskExecution, ID 1 not foundSpring cloud data flow server need to keep the reference of batch jobs tables and if they use different database then it may not be able to resolve the job IDs, hence we need to make sure that both the Batch job application and Cloud data flow server are pointing to same database.
Registering batch application
We can register the application two ways, one is using the Spring cloud data flow server UI dashboard and another is using Shell.
- Using Spring cloud data flow server UI dashboard
-
Open the link http://localhost:9393/dashboard/#/apps in your browser and click on "Add Application(s)" link.
- In below screen select the highlighted option.
- Fill the required details in below screen as given. We have to provide the jar location of our batch application.
- Click on "Register Application" link in below screen to complete the registration.
- Once registration is complete, you can see the job under "App" link as given below.
- Now we need to create a task for same job. Click on "Tasks" link in left navigation and then click the "Create Task(s)" link.
- Then in below screen drag & drop the job from left side pane to right side pane. Then connect it with start and end point. Then click on the "Create Task" button.
- Give a name to your task and click on the create button.
- Once you clicked the create task, it will take you to below screen where you can see the tasks.
- Using Shell
-
Please follow below steps.
- Download the Jar file of shell from below location.
- For latest version, please refer the link https://dataflow.spring.io/docs/installation/
- Once downloaded, execute below command in terminal or command prompt to run the shell application.
java -jar spring-cloud-dataflow-shell-2.2.1.RELEASE.jar
- You will see below output in terminal and shell console to execute the shell commands.
- Now execute below command to register your Batch application Jar with data flow.
app register --name my-batch-job --type task --uri file:////jobs/batch-tutorial-0.0.1-SNAPSHOT.jar
- Then execute below command to create a task of registered batch job.
task create my-batch-job-task --definition my-batch-job
- Now check the data flow server console. You will see the app and task registered with data flow server.
Executing registered task (batch job) using cloud data flow server
Here we have registered our batch job as task which we will execute. It can be done below two ways.- Using Spring cloud data flow server UI dashboard
-
Open cloud data flow task UI dashboard and click on the task you want to run under "Tasks" link.
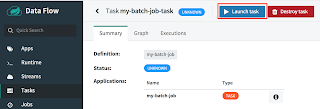
- You will see the below screen. Click on the "Launch" button.
- In this screen you can give the parameter, required to run your job and then select the "Launch the task" button.
- Using shell
-
Run the below command in terminal or command prompt to open the shell terminal.
java -jar spring-cloud-dataflow-shell-2.2.1.RELEASE.jarThen execute the below command to run the task.
task launch my-batch-job-task
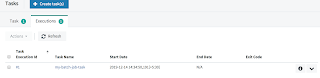
Once task is launched, we can check them at Tasks>Executions on data flow UI dashboard. Click on the ID link to check the status of your task execution.
Then, you will see below screen where you can check the status of your job. Scroll this screen to reach the bottom and there you will see the application execution log of your batch job as given here. In my case I have registered an application with two jobs which you can see in application logs screenshot executed successfully. In ideal scenario we have only one job to execute per application.
Other posts you may like to explore:
Configure multiple datasource with Spring boot, batch and cloud task












Comments
Post a Comment